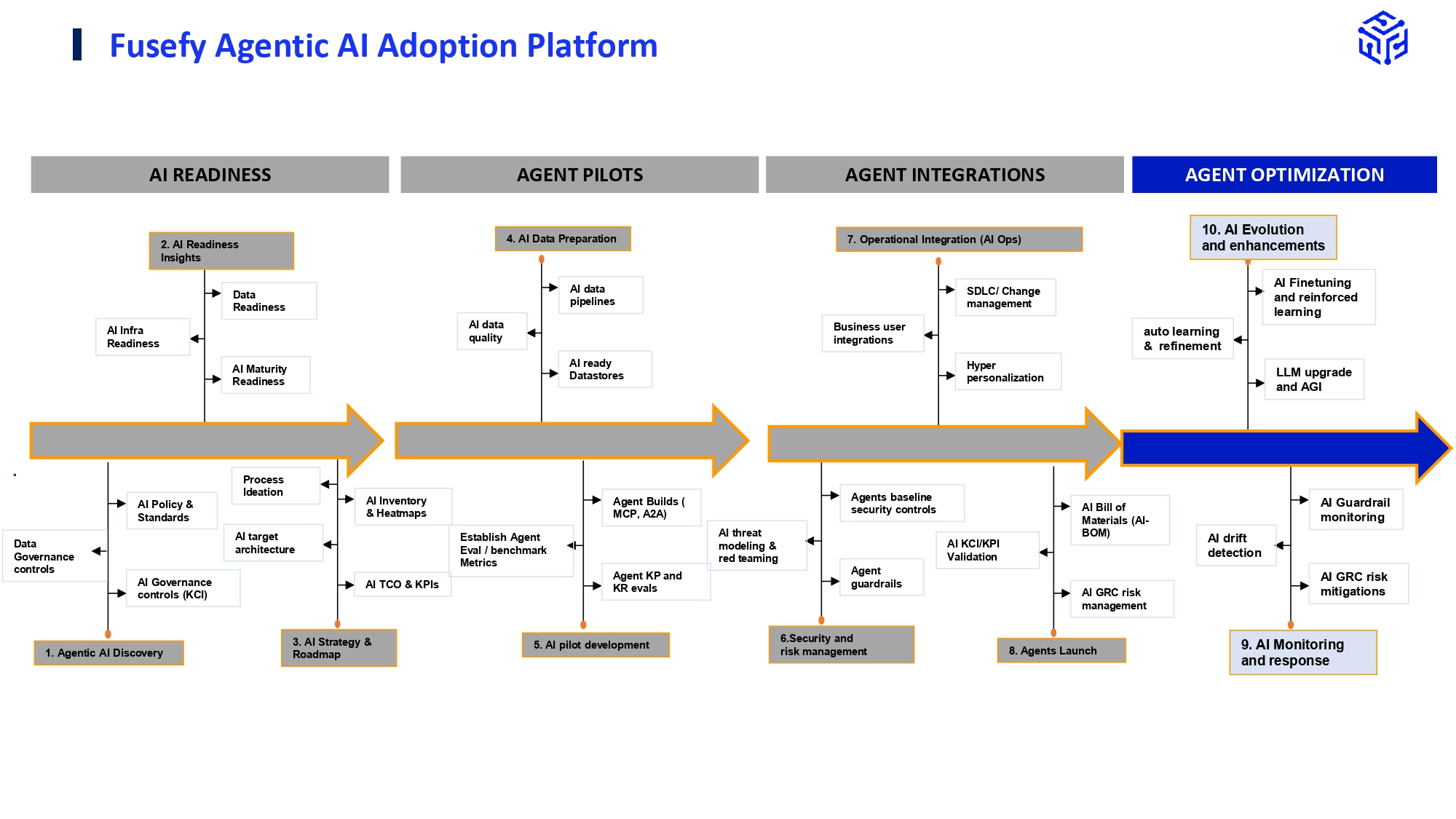
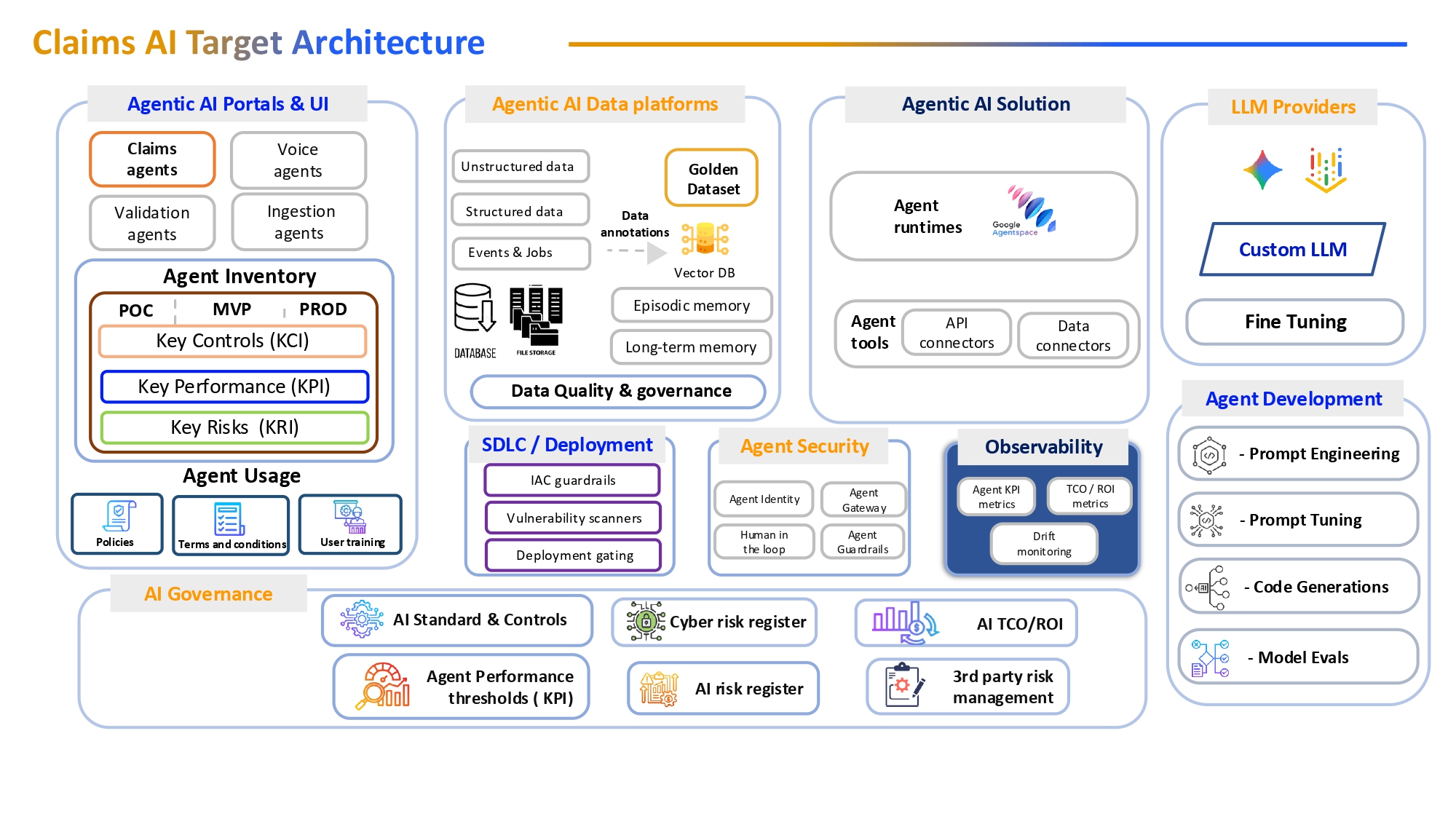
The Enterprise AI Optimization Loop
In our last level, AI Integration, we successfully integrated our AI Fraud Agent. Now, we move into AI Optimization, the continuous loop that ensures an AI system remains trustworthy, accurate, and secure long after its launch. This is where our governance framework becomes an operational process, embedding ongoing vigilance and adaptability into the AI lifecycle.
AI Evolution & Enhancements
The detailed governance and security practices, spanning from Secure SDLC to real-time incident management, are unified by the Enterprise AI Optimization Loop, a dynamic, three-stage operational engine designed to move beyond immediate KRI remediation and ensure sustained KPI improvement. This proactive loop begins with Automated Monitoring & KRI Flagging, systematically feeding emerging risks like model drift directly into a central Risk Register. It is seamlessly followed by Human/Manual Risk Review & Feedback, which integrates expert oversight, facilitates manual risk input, and ensures all remediation actions meet critical regulatory standards (e.g., HIPAA). Finally, Continuous Model Assessment rigorously validates every deployed change via the Secure SDLC, establishing the clear audit trails essential for governance.
Secure SDLC & Change Management in Healthcare Claims
In the context of healthcare claims, the Secure Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) ensures that any changes to AI models, especially those detecting fraud are rigorously managed and auditable. When the KRI (“Model performance degraded due to new fraud patterns”) is flagged, the response follows a formal Secure SDLC process, not a quick patch or hotfix. This is critical because healthcare claims involve sensitive patient data, regulatory compliance (such as HIPAA), and high financial stakes.
Requirement Analysis: The fraud detection team analyzes the new fraud patterns, specifically the novel combination of CPT (Current Procedural Terminology) codes being exploited.
Design & Development: Engineers design new agent logic to recognize these patterns, ensuring the model’s architecture supports both accuracy and explainability for auditors and regulators.
Security Review: The new agent undergoes a security review to ensure it does not introduce vulnerabilities or privacy risks, especially when handling protected health information (PHI).
Testing: The agent is tested in a controlled environment using historical claims data, including the new fraud patterns, to validate its detection accuracy and minimize false positives.
Deployment: Only after passing all security and compliance checks is the agent deployed to production, following change management protocols.
Real-Time Monitoring & Agent Security
Continuous real-time monitoring is essential for detecting anomalies, security threats, and performance degradation in AI agents. In healthcare claims, this includes:
- Agent Behavior Monitoring: Real-time dashboards track agent activity, flagging unusual patterns such as unexpected access to sensitive data, abnormal query volumes, or deviations from expected workflows.
- Prompt Injection Detection: Specialized monitoring tools scan for prompt injection attempts, where malicious actors try to manipulate the agent’s behavior by injecting harmful instructions or data. Automated alerts are triggered if suspicious prompts are detected, and the agent’s permissions are temporarily restricted until the incident is investigated.
- Incident Response: If an agent is compromised via prompt injection or other means, incident management protocols are activated. This includes:
- Immediate revocation of the agent’s permissions to prevent further access or data exposure.
- Isolation of the affected agent for forensic analysis.
- Notification of the security and compliance teams.
- Initiation of a root cause analysis and remediation plan.
- Automated Drift Detection: The system continuously compares current model inputs and outputs against historical baselines. If significant drift is detected (e.g., a sudden increase in false negatives or positives), an alert is generated.
- Root Cause Analysis: The fraud detection team investigates the cause of drift, which could be new fraud patterns, changes in claim submission behavior, or data quality issues.
- Model Retraining: If drift is confirmed, the model is retrained on updated data, following the Secure SDLC process described above.
Revoking Agent Permissions & Incident Management
In the event of a security incident or performance issue, the ability to quickly revoke agent permissions is crucial.
- Permission Revocation: The system supports granular permission controls, allowing administrators to revoke specific agent permissions (e.g., access to PHI, ability to execute certain actions) without disrupting other agents or workflows.
- Incident Management Workflow: A formal incident management workflow is triggered when an agent is compromised or underperforms. This includes:
- Immediate containment (e.g., revoking permissions, isolating the agent).
- Investigation and root cause analysis.
- Remediation (e.g., patching, retraining, redeploying).
- Post-incident review to update policies and prevent recurrence.
Traceability & Artifact Management in Healthcare Claims
Traceability and artifact management are essential for regulatory compliance and operational transparency in healthcare AI systems.
- Versioning: The new fraud detection agent is versioned as FraudAgent-v1.1-prod. This versioning allows stakeholders to clearly identify which model is active and when it was deployed.
- AI Asset Inventory: The agent and its associated artifacts (training data, model weights, configuration files) are logged in the AI Asset Inventory. This inventory is part of the broader traceability solution, ensuring every change is documented and auditable.
- Lineage Tracking: The lineage of FraudAgent-v1.1-prod is tracked, showing:
- The source of the new training data (including the specific CPT code combinations).
- The development and testing environments used.
- The deployment timeline and responsible teams.
- Rollback Capability: If the new agent underperforms or introduces unintended consequences, the system can roll back to FraudAgent-v1.0-prod. This rollback is supported by the versioned artifacts and documented change history.
By embedding this disciplined process, your organization transforms AI system maintenance from a reactive cost center into a strategic asset, securing traceability and aligning every AI modification with risk management and compliance goals in healthcare claims processing. This integrated approach ultimately strengthens your ability to detect and respond to new fraud patterns faster, maintain regulatory compliance, provide clear audit trails, and deliver demonstrable improvement in the overall KPI for fraud detection accuracy and operational efficiency. This is the foundation of truly scalable, trustworthy AI.