The Enterprise AI Integration
When our AI Fraud Agent completed its pilot run and hit a 95% precision KPI in a safe, data-masked environment, we begin with AI Integration. In this level, the AI connects to the live production system, gains access to real Protected Health Information (PHI), and begins influencing actual claim decisions. This stage is all about enforcing production-grade controls — the technical, procedural, and ethical safeguards that ensure our AI acts responsibly in the real world.
1. Pre-Flight Checks: Hardening for Production
Before going live, every component of our system passes a rigorous series of Key Control Indicators (KCIs). Each KCI is security-driven because once real PHI enters the equation, system design alone isn’t enough; resilience, auditability, and containment become non-negotiable.
Authentication & Authorization (RBAC):
The “Adjuster Dashboard” integrates with corporate Single Sign-On (SSO). Human adjusters authenticate through the enterprise identity provider. Then, Role-Based Access Control ensures that each adjuster can view only their assigned claims. Authentication confirms who they are; authorization defines exactly what they can touch.
Secret Management:
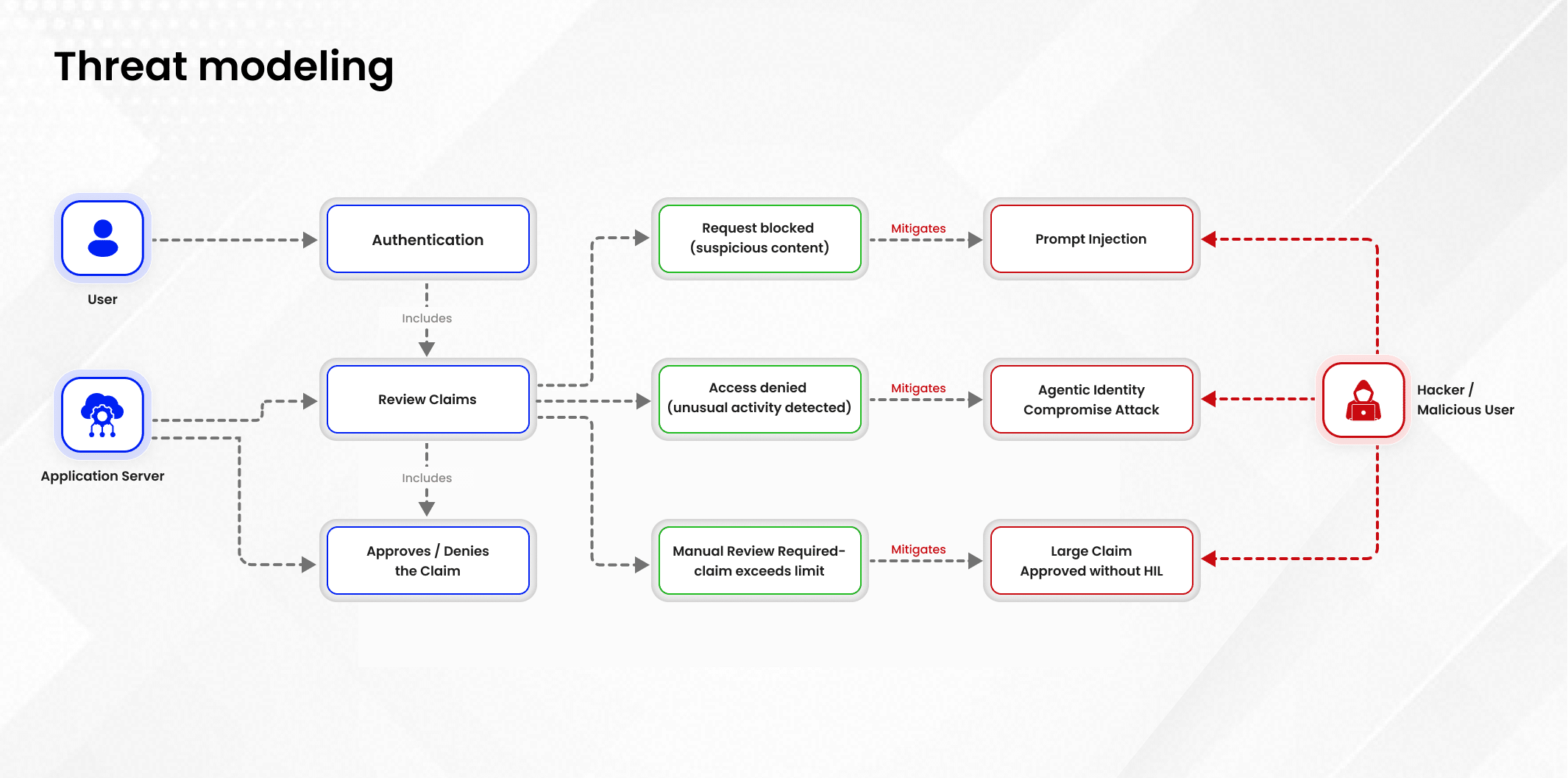
The Fraud Agent gets its own agent identity to ensure agent actions are attributable and revoked if there is a compromise. This eliminates “Confused Deputy” risks often seen in AI deployments.
Network Security & Zero trust:
The agent migrates from a sandbox to a production enclave governed by Zero Trust principles. Every network call is verified; every access request is validated. The agent can only reach pre-approved endpoints defined in its authorization policy — typically the claims database and a limited fraud-checking API set. This limits blast radius even in case of anomalous behavior.
Threat & Vulnerability management:
Before deployment, the dashboard, model-serving API, and backend integrations are all scanned for known vulnerabilities. Patches are mandatory before release gates clear, creating a baseline of system hygiene.
Offensive Security Testing (AI Red Teaming)
The final test simulates attackers. Our red team attempts adversarial prompts, injection attacks, and data exfiltration attempts. Only when the system can detect, reject, and recover from these prompts does it earn a green light for go-live. This ensures our model behaves predictably even when provoked by malicious users or corrupted data entries.
2. Go-Live: The Human-in-the-Loop (HITL) Dashboard
The Fraud Agent now reads real PHI but power remains moderated through the Human-in-the-Loop (HITL) design.
Human-in-the-Loop & Consent:
The AI never autonomously denies claims. Instead, it surfaces flagged cases to the human reviewer, strengthening both accountability and fairness. The adjuster dashboard summarizes outcomes:
“850 claims auto-approved. 150 flagged for review.”
Decision transparency is built directly into the workflow.
AI Evaluation & Explainability
Every flagged claim comes with a reason.
Example:
“Flagged Claim [ID-456]: CPT code (99214) does not match diagnosis code (S93.401A). Suggest: Downgrade to 99202.”
This explainability layer transforms the AI from an opaque scorer into a collaborative assistant, making model behavior auditable for both compliance and learning purposes.
By fusing precision with explainability, we transform fraud detection from a black box to a guided partner for healthcare adjusters, all without compromising patient privacy.
3. Activating Production Guardrails and Monitoring
Once the system is live, our guardrails and monitors never rest. Security has to be a continuous posture while deploying AI systems in regulated sectors like healthcare.
Input/Output Guardrails:
Real-world data is messy and unpredictable. Input guardrails intercept malicious pattern attempts (for instance, a prompt injection buried in a “notes” field). Output guardrails sanitize the model’s explanations, ensuring no PHI leaks into system logs, dashboards, or audit feeds.
Model & Data Monitoring:
The same precision KPI (95%) from pilot mode now runs in continuous tracking. A signal of stability may continue for a period and if there is a drop in the model precision, it triggers a Key Risk Indicator (KRI): “Model Performance Degraded.” The system automatically escalates this anomaly.
Incident Response Plan & Risk register:
When a KRI triggers, the safeguard chain engages. The AI Risk Register logs a high-priority incident, invoking the Incident Response Plan. The response team investigates potential causes: data drift, new claim types, or adversarial behavior. Every discovery rounds back into our evolving risk taxonomy.
These mechanisms ensure that once AI is deployed,governance doesn’t weaken but scales alongside it.
By now, our Fraud Agent operates as a trusted production system, and the newly logged KRI becomes the opening note for our next level: AI Optimization.
In Level 3, we’ll dive into how our teams close the loop — retraining models, refining policies, and strengthening resilience so that compliance, security, and performance continuously reinforce each other. This final step is what transforms an AI from a high-performing model into a Trustworthy system.